The Power of Artificial Intelligence for Robotics: Redefining Manufacturing

July 20, 2023

The field of robotics has grown exponentially over the past few decades. However, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is giving rise to a new era of manufacturing possibilities. By understanding what AI is and how it relates to manufacturing and robotics, we can begin to explore its transformative potential.
In this article, we’ll look at the evolving landscape of robotics and manufacturing, shaped by the power of artificial intelligence (AI).
We find it incredibly exciting to delve into the immense possibilities that AI, particularly when integrated with robots, presents for the future.
These technological advances hold great promise for revolutionizing manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency, safety, and productivity. So, let's explore what these advancements can mean for the emergence of new technologies in the robotics and manufacturing space.
| Table of Content |
What is AI?
AI refers to a branch of computer science that involves creating smart machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning from experience, understanding complex data, recognizing patterns, solving problems, and making decisions.
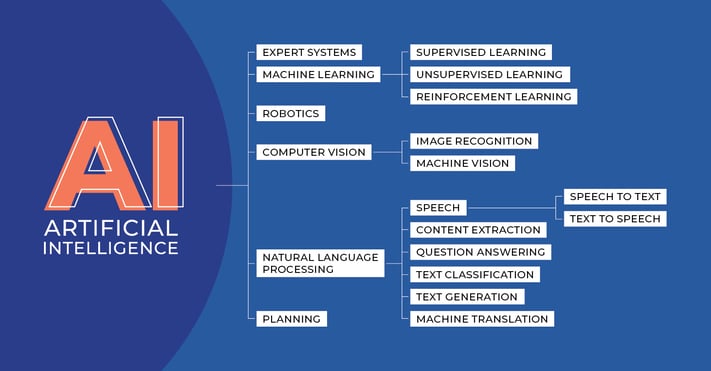
AI vs Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are two terms that are often used interchangeably but have distinct meanings, especially in the context of robotics and manufacturing.
Machine Learning is a subset of AI. It is a specific method of achieving AI, focusing on the idea that machines should be given access to data and allowed to learn and improve from it. In other words, ML algorithms use computational methods to "learn" information directly from data without relying on a predetermined equation as a model.
In the realm of robotics and manufacturing, AI serves as the foundation for creating intelligent systems that can understand, learn, and adapt to their environment. Machine Learning provides the mechanisms for these systems to automatically learn and improve from experience.
For instance, a robot can use machine learning to optimize its operations, learn from past mistakes, predict future trends, and, thus, improve its efficiency and effectiveness in the manufacturing process.
AI vs. Computer Vision
Computer Vision is also a subfield of AI that focuses on enabling machines to "see", understand, and interpret visual data from the real world.
In the context of robotics and manufacturing, Computer Vision can help robots recognize and manipulate objects, navigate through space, and perform quality control by detecting defects.
In essence, while AI serves as the "brain" that enables robots to learn, adapt, and make decisions, Computer Vision acts as the "eyes" that allow robots to perceive and interpret their environment.
AI vs. NLP (Natural Language Processing)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is another subfield of AI. It focuses on enabling machines to understand and generate human language. NLP can allow robots to understand instructions given in natural language, making human-robot interaction more intuitive.
While AI provides the overall intelligence framework for robots, NLP specifically enhances their linguistic understanding capabilities.
In manufacturing settings, this can mean smoother and more effective communication between operators and machines, facilitating quicker adaptation to new tasks and processes.
AI vs Robotics
AI and Robotics, though distinct, are two interconnected domains. Robotics involves designing and creating robots that can interact with the physical world. AI, on the other hand, is about creating intelligent machines. When combined, AI brings the "intelligence" to the physical constructs of robotics.
In the manufacturing industry, robots perform physical tasks such as assembling parts or moving items. The integration of AI can enhance these physical tasks by enabling the robots to learn from their experiences, make decisions based on their surroundings, and adapt to new tasks quickly.
It's this combination of AI and Robotics that is driving the next revolution in manufacturing.
The actual use of these technologies in robotics varies significantly. For example, machine learning can be used to optimize robotic movements in a production line, while AI can be used to make complex decisions based on a variety of factors in their environment.
| Key Takeaway |
|
|
Actual Uses of AI Technologies for Robotics
AI technologies have a wide range of applications for robotics. A few examples include:
- Advanced Image Recognition: Robots equipped with AI-powered vision can interpret the physical world more accurately, enabling tasks such as quality inspection or component sorting.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing data trends, AI can predict when a machine is likely to fail, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Adaptive Learning: Robots can improve their performance over time, adjusting to new information or changes in the environment.
How AI Can Impact Manufacturing and Robotics
|
|
|
| Process Improvement |
AI algorithms can analyze massive amounts of data to identify and implement efficiency improvements. This can lead to significant cost savings and increased production output. Predictive maintenance powered by AI can foresee and prevent machinery breakdowns, minimizing downtime. |
| Enhanced Quality Control |
AI-enabled robots can detect and correct production errors in real-time, reducing waste and improving overall product quality. AI can also monitor and maintain quality standards consistently, eliminating human error. |
| Increased Flexibility |
AI can swiftly reprogram robots for different tasks, enabling rapid changeovers between various products. This is particularly crucial in today's manufacturing environment, where customization and adaptability are key. |
| Workflow Planning and Scheduling |
By analyzing various data points like job orders, material availability, and manpower, AI can aid in creating optimal workflows. This results in better resource utilization and faster job completion. |
AI and Welding Automation
Welding is a fundamental process in many manufacturing sectors, and AI has the potential to revolutionize it.
AI can influence three critical aspects of welding automation:
Automation Task Setup
AI can assist in training, teaching, and programming robots to perform complex welding tasks with precision. AI can learn from a series of inputs and refine its approach over time.
When applied to welding, AI systems can fine-tune their own parameters for speed, heat, and angle of welding, making micro adjustments where necessary. This helps to create consistent, high-quality welds, regardless of the complexity of the task.
Traditional programming of robotic systems can be time-consuming and require specialized knowledge. With AI, systems can be trained using a variety of methods, such as demonstration or through learning from simulation, reducing the time and expertise required for setup.
AI-powered robots can adapt to changes in the manufacturing process more efficiently. If a product design is altered or a new product is introduced, the AI system can quickly learn the new welding requirements, making production lines more flexible and responsive to changes.
Process Optimization
Combining AI and vision systems can optimize welding settings for each specific job, leading to higher quality welds and fewer wasted materials. With AI-powered vision systems, robots can visualize and comprehend the welding environment in real-time, much like a human welder would.
This includes recognizing spatter, a common challenge in welding, and adjusting parameters on the fly to mitigate it. This ensures a cleaner, more precise weld and reduces post-welding clean-up.
AI-backed vision systems can also identify and track the joint being welded. As a result, the robot can automatically adjust its path and maintain an optimal position and angle at all times, even when dealing with complex, variable joints. This not only increases the quality of the weld but also expands the range of welding tasks that can be automated.
Predictive Maintenance and IoT 4.0
Connecting welding equipment and robots to the Internet of Things (IoT) allows for vast amounts of data to be collected and analyzed. This data can help predict maintenance needs, further improving efficiency and uptime.
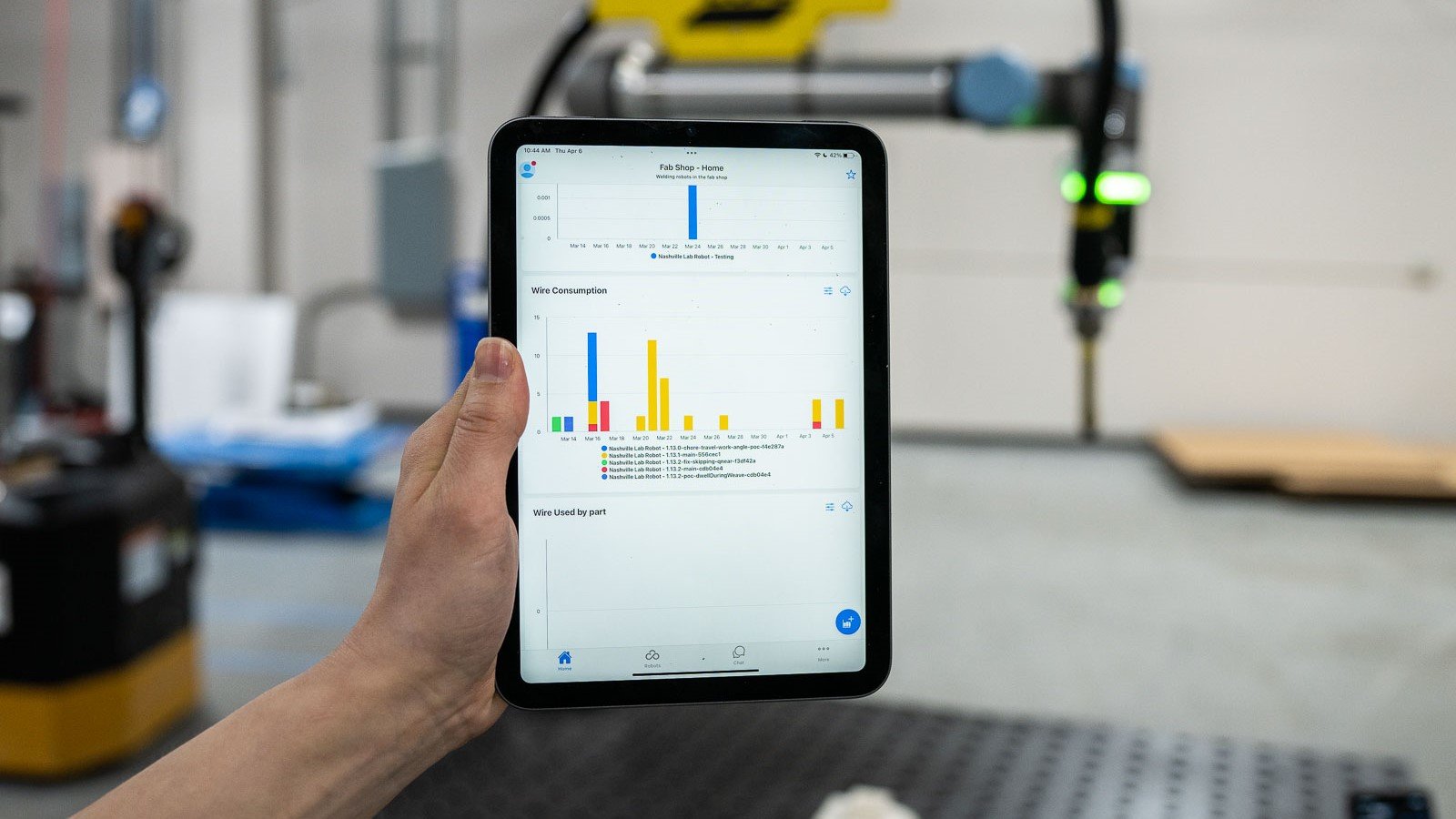 Hirebotics' Cobot Welder is a cloud-connected welding cobot offering real-time productivity data.
Hirebotics' Cobot Welder is a cloud-connected welding cobot offering real-time productivity data.
Real-time data about the performance and condition of robots and welding equipment can be constantly monitored with sensors. This data can include information about the machine's temperature, vibration levels, power consumption, and more.
AI steps in by analyzing this data to identify patterns and anomalies. It can predict when a component might fail or when the machine will need servicing. This is the crux of predictive maintenance - addressing maintenance needs before they result in downtime, based on data-driven predictions.
AI can also optimize maintenance schedules based on usage patterns and predicted needs, ensuring that maintenance activities cause minimal disruption to production. It can suggest tweaks to machine settings or alert operators to suboptimal operation, helping to improve the overall efficiency of the welding process.
Navigating the Future: Addressing the Concerns of AI in Robotics and Manufacturing
The implementation of AI in robotics and manufacturing is a transformative movement, unlocking new efficiencies and capabilities.
However, as with any groundbreaking technology, there are considerations to be addressed to ensure successful integration.
1. Initial Investment and Ongoing Costs
While AI-powered solutions may require an initial investment that may be higher than traditional systems, it's essential to consider the long-term savings these solutions offer.
Through efficiencies such as improved output, reduced waste, and minimized downtime, AI can substantially lower operational costs over time.
2. Cybersecurity and AI
Increased connectivity, while a potential cybersecurity concern, is also an opportunity to bolster defenses using AI itself.
AI can proactively identify threats, safeguarding data integrity and ensuring system resilience. While robust cybersecurity protocols are needed, AI provides tools to enhance these protections.
3. Dependence on Vendors
While reliance on vendors for AI solutions is a consideration, this relationship also offers access to continual upgrades, expert maintenance, and troubleshooting support.
This collaboration ensures your systems remain cutting-edge and operate at peak performance.
4. Technological Complexity
Although AI solutions may initially appear complex, they are designed to simplify processes and improve user experience over time.
User-friendly interfaces, alongside targeted training programs, make AI a powerful, accessible tool for staff at all levels.
5. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
In a rapidly evolving tech landscape, staying compliant with regulations can seem daunting.
However, AI systems can help track changes and ensure adherence to these regulatory updates, turning a potential challenge into another avenue where AI assists businesses.
The adoption of AI in robotics and manufacturing represents an exciting step towards the future. By understanding and addressing these considerations, manufacturers can harness the full power of AI, opening the door to unparalleled levels of innovation and efficiency.
Last Thoughts About AI and Robotics
Artificial Intelligence has emerged as a powerful tool for transforming the landscape of robotics and manufacturing. Its role extends from streamlining operations and enhancing human-robot interaction to driving process improvements in areas such as welding automation.
AI can simplify programming and operation in manufacturing settings, enhancing communication and improving efficiency. With technologies like GPT-3, robots can understand natural language, facilitating real-time decision-making and adaptive learning.
The application of AI in areas like welding automation is particularly promising. By enabling precise control, real-time quality inspection, enhanced safety measures, and optimal process automation, AI can significantly elevate the standards of welding practices with new robotic welding technologies.
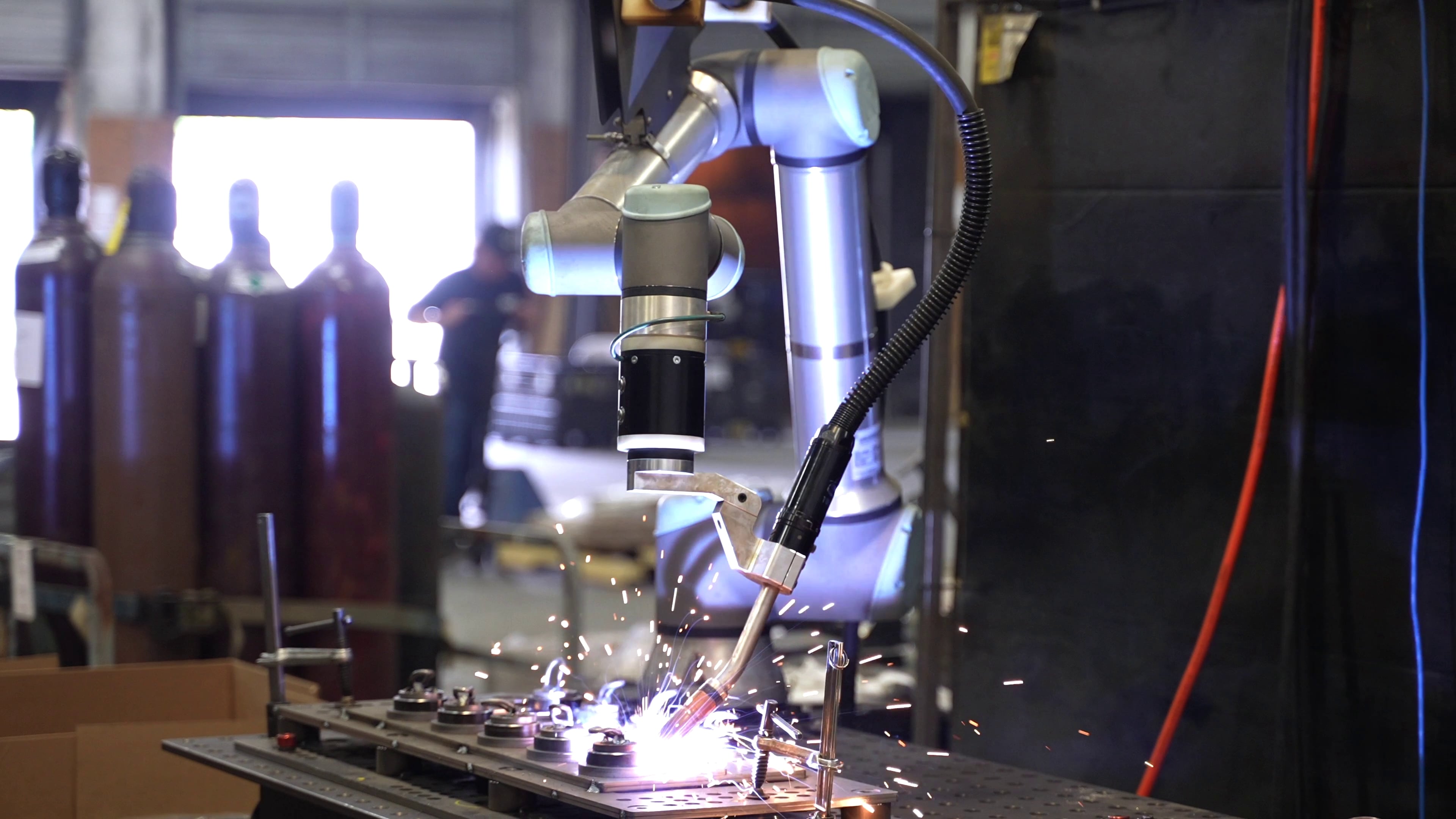 Hirebotics' Cobot Welder has impacted many manufacturing businesses over the last few years.
Hirebotics' Cobot Welder has impacted many manufacturing businesses over the last few years.
While integrating AI can be highly beneficial, it's crucial to effectively manage the challenges that come with it. These may include a significant upfront investment, the reliance on data, as well as uncertainties surrounding regulations.
Integrating AI into robotics and manufacturing may pose some challenges, but the rewards and possibilities it presents to these fields are boundless, leading the way to a promising future.
It is an opportunity to redefine processes, boost productivity, and drive a new era of growth and innovation.
Harness the Power of Cobots with Hirebotics
At Hirebotics, we're at the forefront of robotic innovation, empowering businesses like yours with cutting-edge solutions.
With Hirebotics’ unique phone app and quick response support, our Cobot Welders are easy to implement and program. They're perfect for small batch production or tasks requiring high precision. Cobots provide an effective way to bridge the gap between fully manual labor and complete automation, combining the best aspects of both worlds.
Contact us today at Hirebotics, and let's explore how our welding cobots can transform your operations and take your productivity to the next level.



